How to Find Cumulative Frequency
Here is a frequency distribution table FDT for a small data set. You can create more than cumulative frequency by subtracting the frequency of the second-class from the first class and so on.
Percentage Cumulative Frequency How To Youtube
To construct a cumulative frequency distribution table there are a few steps that can be followed which makes it simple to construct.
. Then add up the number of times each value appears in the data set or the absolute frequency of that value. The more tests we do during an experiment the observed relative frequency of an event will get closer to the theoretical probability of the event. But when looking at acceleration values the higher frequency content dominates and on the flip side when looking at displacement the low frequency content dominates.
This calculation is important in statistics because it shows how the percentages add together over a time period. We can also create an. If you are just asked for frequency from the relative frequency it probably means the absolute frequency.
Find the central tendency of your data. B Find the median height. Because velocity corresponds to energy this tends to be the primary metric tracked over time for vibration health monitoring for condition-based and predictive maintenance.
Cumulative Frequency is an important tool in Statistics to tabulate data in an organized manner. Cumulative frequency distributions. In the image below Column D shows the formulas we used.
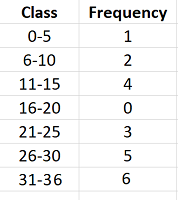
As we know that the cumulative frequency curves are created using the cumulative frequencies so in more than cumulative frequency curve the frequencies of succeeding class or interval are added to the current class or interval frequency. Frequency distributions are often displayed. Next we will calculate the cumulative frequency of each class in column C.
Total for question 1 is 3 marks Height Cumulative Frequency 140 h 150 7 140 h 160 17 140 h 170 32 140 h 180 51 140 h 190 57 140 h 200 60 a On the grid plot a cumulative frequency graph for this information. For example if a person has data on how many times it snowed in January he would then add the data from February to tell the cumulative percentage of days. Whenever you wish to find out the popularity of a certain type of data or the likelihood that a given event will fall within certain frequency distribution a.
This frequency can be varied every time we repeat the experiment. Find the cumulative frequency distribution. It may be helpful to build a relative frequency table.
Heres a detailed example of how to find cumulative frequency for successful trials step-by-step. How to find relative frequency for the 4 14 16 22 24 25 37 38 38 40 42 42 45 44 with 4 number of groups. The following example illustrates how to find cumulative frequencies in Excel.
Cumulative Frequency in Excel. Youve just defined the starting point in Cell C2 to calculate cumulative frequency. That is the cumulative frequency is as its definition requires the cumulative sum of just one.
Cumulative definition increasing or growing by accumulation or successive additions. Cumulative relative frequency is the accumulation of the previous relative frequencies. Heres how to find cumulative relative frequency.
Create a relative frequency distribution. Adjective increasing by successive additions. You will learn how to see frequencies of different variables find the mostleast commonly occurring values in your data check for missing values Let.
Understand the variability of. Add B3 with C2. Find the frequency for each class interval.
1 The cumulative frequency table shows the height in cm of some tomato plants. Tap on the Cell B2. First we will enter the class and the frequency in columns A and B.
To calculate cumulative frequency start by sorting the list of numbers from smallest to largest. The cumulative effect of one rejection after another. Cumulative frequency analysis is the analysis of the frequency of occurrence of values of a phenomenon less than a reference value.
Made up of accumulated parts. Cumulative Frequency Revision Notes. Since the sum of the masses must be 1 these constraints determine the location and height of each jump in the empirical CDF.
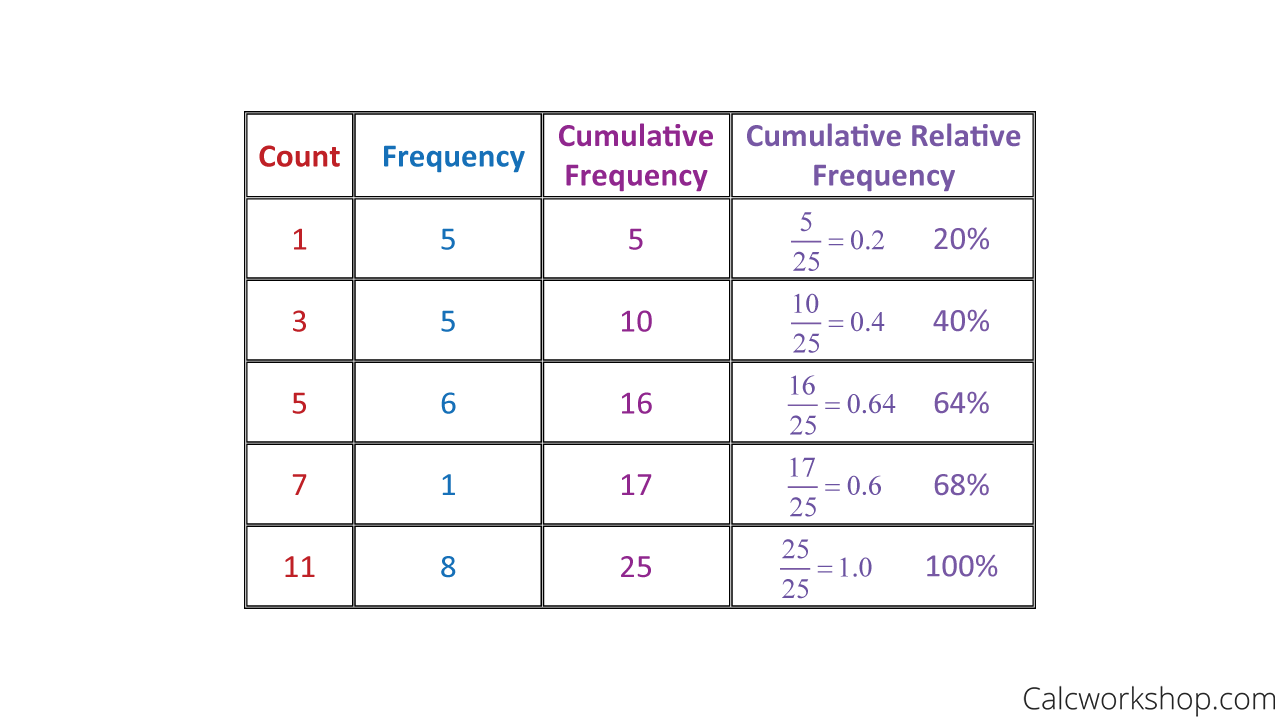
Take your relative frequency and multiply it by the total number of items in the full data set and you will have the absolute frequency. Maths revision video and notes on the topic of Cumulative Frequency. The sum of the frequencies less than or equal to each value or class interval of a variable.
Select Cell C2. Cumulative percentages add a percentage from one period to the percentage of another period. Use the continuous variables to set up a frequency distribution table using a suitable class length.
Data value frequency 13 10 14 12 15 16 16 30 17 18 Find the following measures of central tendency. It can be achieved using different techniques grouped ungrouped cumulative relative and relative cumulative types based on the data being handled. To better understand your datas distribution consider the following steps.
Next find the cumulative frequency of each number by counting how many times that value or a smaller value shows up in the data set. Cumulative frequency begins at 0 and adds up the frequencies as you move through your list. The empirical distribution function is a formal direct estimate of the cumulative distribution function for which simple statistical properties can be derived and which can form the basis of various statistical hypothesis tests.
You can use this type of frequency distribution for ordinal or quantitative variables when you want to understand how often observations fall below certain values. Now go to Cell C3. The empirical cumulative distribution function is a CDF that jumps exactly at the values in your data set.
Mean xx Please show your answer to one decimal place median Please enter an exact answer mode Please enter an exact answer. Edexcel Exam Papers OCR Exam Papers AQA Exam Papers. How to make a frequency table.
The cumulative sum produced by the sum function treats all the missing values produced by the previous command as 0 which is precisely what we want. Firstly the frequency table maker generates a table according to the given number of groups. Add the relative frequencies of previous data points to the relative frequency of the current item.
Find the experimental probability for every item in the dataset using the relative frequency formula. Construct a histogram cumulative frequency histogram and a box-and-whisker plot given a set of data Frequency Histogram Definition Histograms Quartiles Understand how the five statistical summary minimum maximum and the three quartiles is used to construct a box-and-whisker plot Quartiles Create a scatter plot of bivariate data Scatter Plots. Let us see what the steps are.
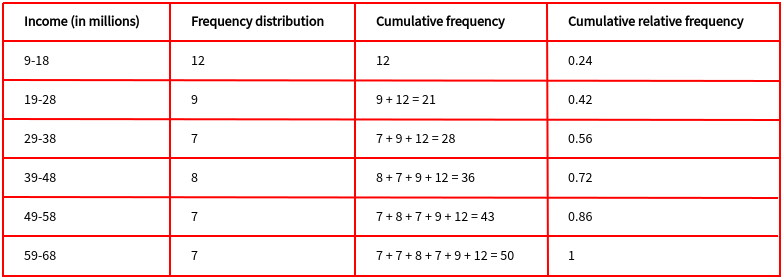
In this article we will show you 7 different ways to analyze your data using the FREQ procedure. So heres our data below in the picture where you have to find Cumulative Frequency as well as Cumulative Percentage in two specified columns. It is the CDF for a discrete distribution that places a mass at each of your values where the mass is proportional to the frequency of the value.
The cumulative relative frequency of. Making a frequency table is only the first step in understanding the distribution of values in your dataset. A Level Revision.
A Level Revision A Level Modular Revision. Frequency distribution a function in statistics is used to reflect the different results of a particular frequency in the form of a table andor graph depicting how many times a specific value has appeared in a group or an interval.

Lesson Explainer Cumulative Frequency Graphs Nagwa

Cumulative Frequency Distribution Simple Definition Easy Steps
Comments
Post a Comment